Samsung’s Competitive Edge in HBM4 Memory Technology
Summary:
- Market Status: Samsung has fallen behind SK Hynix and Micron in the HBM memory sector but aims to reclaim its position with HBM4 technology.
- Technological Advances: Samsung’s HBM4 delivers impressive performance boosts, achieving a frequency of 11Gbps—37.5% higher than the standard.
- Future Prospects: The company’s success hinges on production capacity and competitive pricing to secure contracts with major clients like NVIDIA and AMD.
In the competitive landscape of High Bandwidth Memory (HBM), Samsung has recently emerged as the third player to achieve mass production, trailing behind industry leaders SK Hynix and Micron. However, the South Korean tech giant is setting its sights firmly on the cutting-edge HBM4 technology to regain its competitive edge.
Recent Developments in Samsung’s HBM Technology
As of September 21, it was revealed that Samsung had finally attained certification for its HBM3e from NVIDIA after 18 months of mass production. This milestone follows the prior certification from AMD, solidifying its credibility in the market. Despite these accomplishments, the company faces an uphill battle due to SK Hynix’s advantageous position as the first mover in the HBM3e category. Samsung’s main focus now appears to be on the latest and most advanced HBM4 memory technology.
HBM4: A Leap Ahead
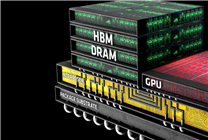
Notably, SK Hynix has made headlines by achieving global mass production of HBM4, yet it still employs fifth-generation 10nm-level technology in its production. In contrast, Samsung has taken a more aggressive approach, implementing the sixth-generation 10nm DRAM process—termed 1c—in its Pyeongtaek P5 factory. This advanced technology has allowed Samsung to significantly enhance the performance of its HBM4 offerings.
Through rigorous development alongside its 4nm logic process, Samsung has boosted the frequency of its HBM4 memory to an impressive 11Gbps. This represents a substantial 37.5% increase in performance compared to the standard 8Gbps HBM4 memory.
Strategic Partnerships and Market Implications
In preparation for the launch of AMD’s MI450 series AI graphics cards in the upcoming year, NVIDIA has requested its suppliers to target a frequency of 10Gbps for HBM4. Samsung, having already surpassed this requirement with its 11Gbps capability, positions itself advantageously to secure orders from NVIDIA.
While Samsung’s technical advancements indicate a remarkable comeback, the company’s ability to clinch contracts with major industry players like NVIDIA and AMD will depend on several factors. These include their ability to scale production and maintain competitive pricing in a rapidly evolving market.
Looking Ahead
As the battle for dominance in the HBM memory market intensifies, Samsung’s concerted efforts in advancing HBM4 technology reveal its commitment to regaining leadership in the semiconductor space. The strategic importance of HBM4 cannot be overstated—it is crucial for high-performance computing applications, AI, and gaming technologies, where speed and efficiency are paramount.
In conclusion, while Samsung has made impressive strides in HBM memory production, the journey ahead is laden with challenges. Market dynamics, technological advancements by competitors, and pricing strategies will dictate whether Samsung can reclaim its former glory in the memory landscape. The next few months will be telling as the technology reaches the market, and demand from industry giants evolves.
For more updates and the latest insights into technology trends, stay tuned to industry news sources.