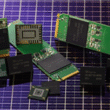
Intel Revolutionizes Heat Sink Assembly for Advanced Packaging Chips
Summary:
- Intel has developed a novel method to simplify heat sink assembly.
- This innovation enhances heat dissipation and reduces production costs.
- The approach is pivotal for manufacturing "super large" advanced packaging chips.
In a significant breakthrough for semiconductor manufacturing, Intel researchers have unveiled a method that transforms the way heat sinks are assembled for advanced packaging chips. This innovative technique streamlines the manufacturing process, making it both more economical and proficient in thermal management—an essential aspect of high-power chip design.
Simplifying Complexity in Thermal Management
The new assembly approach focuses on disassembling complex heat sink designs into simpler components. This method allows for the efficient assembly of heat sinks using traditional manufacturing processes, significantly reducing both complexity and associated costs. Specifically outlined in recent research, the disassembled design not only facilitates easier manufacturing but also enhances heat dissipation for next-generation chips, particularly those that operate at high temperatures.
Advantages of the New Methodology:
- Reduced Manufacturing Difficulty: By breaking down the heat sink into simpler units, Intel minimizes the intricacies typically involved in assembling high-performance thermal solutions.
- Enhanced Thermal Efficiency: The new design promises improved heat distribution, crucial for chips that are increasingly demanding when it comes to thermal management.
- Cost-Effectiveness: This simplified assembly reduces reliance on expensive machining and complex manufacturing techniques, driving down production costs significantly.
Technical Insights
Intel’s advanced packaging technology is particularly adept at supporting multi-layer stacking and various chip combinations. The implementation of this new assembly method has demonstrated promising results, including a 30% reduction in package warpage and a 25% decrease in the void rate of thermal interface materials. Such enhancements are vital for developing "super large" chips that traditional manufacturing techniques struggle to support.
Key Features of the Disassembled Heat Sink Design:
- Optimization of Thermal Interface Materials: The new assembly utilizes advanced adhesives and flat sheets, alongside improved reinforcements to boost thermal conduction capabilities.
- Flat Plate Structure: The primary component of the heat sink offers an optimal surface for heat dissipation, while additional reinforcements maintain the necessary flatness across varying chip architectures.
- Facilitated Production: Components can be fabricated through standard stamping processes, negating the need for costly special equipment.
Addressing Manufacturing Challenges
Today’s high-performance CPUs and GPUs are typically equipped with a metal heat sink situated above the main chip, effectively transferring heat to the integrated heat spreader and ultimately to the radiator system. However, challenges arise when chip sizes exceed 7,000 square millimeters—traditional manufacturing techniques, such as stamping, struggle to form the intricate shapes required, leading to higher costs and prolonged supply cycles.
The innovative disaggregated approach resolves these manufacturing roadblocks by dispersing the heat sink into easily assembled parts during the packaging phase. The flat plate serves as the key area for heat dissipation, while reinforcements ensure the overall integrity and flatness of the assembly, paving the way for innovative chip designs.
Enhancing Performance and Future Applications
The new assembly technique promises to improve package coplanarity by approximately 7%, resulting in a smoother chip surface post-installation of the reinforcement. This precision further boosts overall performance and functionality, marking a significant advancement in chip packaging technology.
In addition, Intel’s engineers have plans to extend this modular approach to professional cooling solutions, including metal composite radiators that offer high thermal conductivity and liquid cooling systems. This strategic pivot suggests a bold future for cooling technologies in high-performance applications.
Conclusion
With its innovative heat sink assembly method, Intel is positioning itself at the forefront of semiconductor manufacturing efficiency and thermal management. By simplifying an essential component of high-power chip design, the company’s advancements not only pave the way for groundbreaking packaging technologies but also promise substantial cost savings and enhanced performance. As the industry leans further into the complexities of chip architectures, Intel’s research may very well define the future of heat management in advanced semiconductor solutions.